AWS Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a prompting technique that supplies domain-relevant data as context to produce responses based on that data and the prompt.
This technique is similar to fine-tuning.
However, instead of having to fine-tune a foundation model with a small set of labeled examples, you can use RAG to retrieve a small set of relevant documents from a large corpus and provide context to answer questions.
RAG doesn't change the weights of the foundation model, whereas fine-tuning changes model weights.
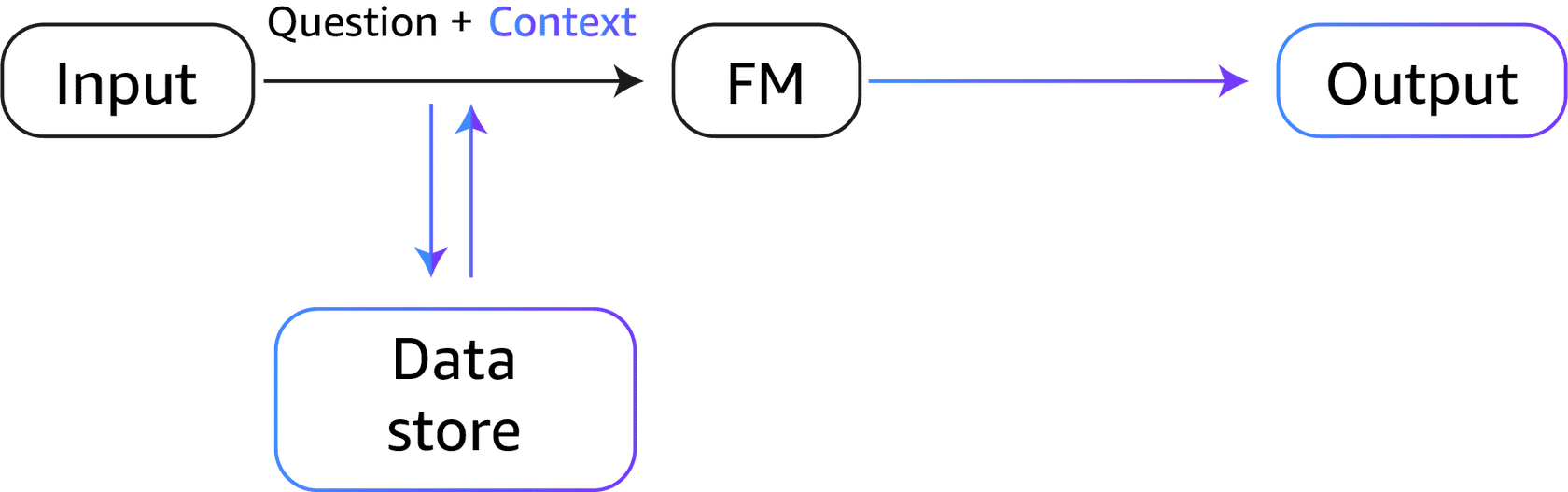
This approach can be more cost-efficient than regular fine-tuning because the RAG approach doesn't incur the cost of fine-tuning a model.
RAG also addresses the challenge of frequent data changes because it retrieves updated and relevant information instead of relying on potentially outdated sets of data.
In RAG, the external data can come from multiple data sources, such as a document repository, databases, or APIs.
Before using RAG with LLMs you must prepare and keep the knowledge base updated.
The following diagram shows the conceptual flow of using RAG with LLMs. To see the steps the model uses to learn once the knowledge base has been prepared, choose each of the four numbered markers.
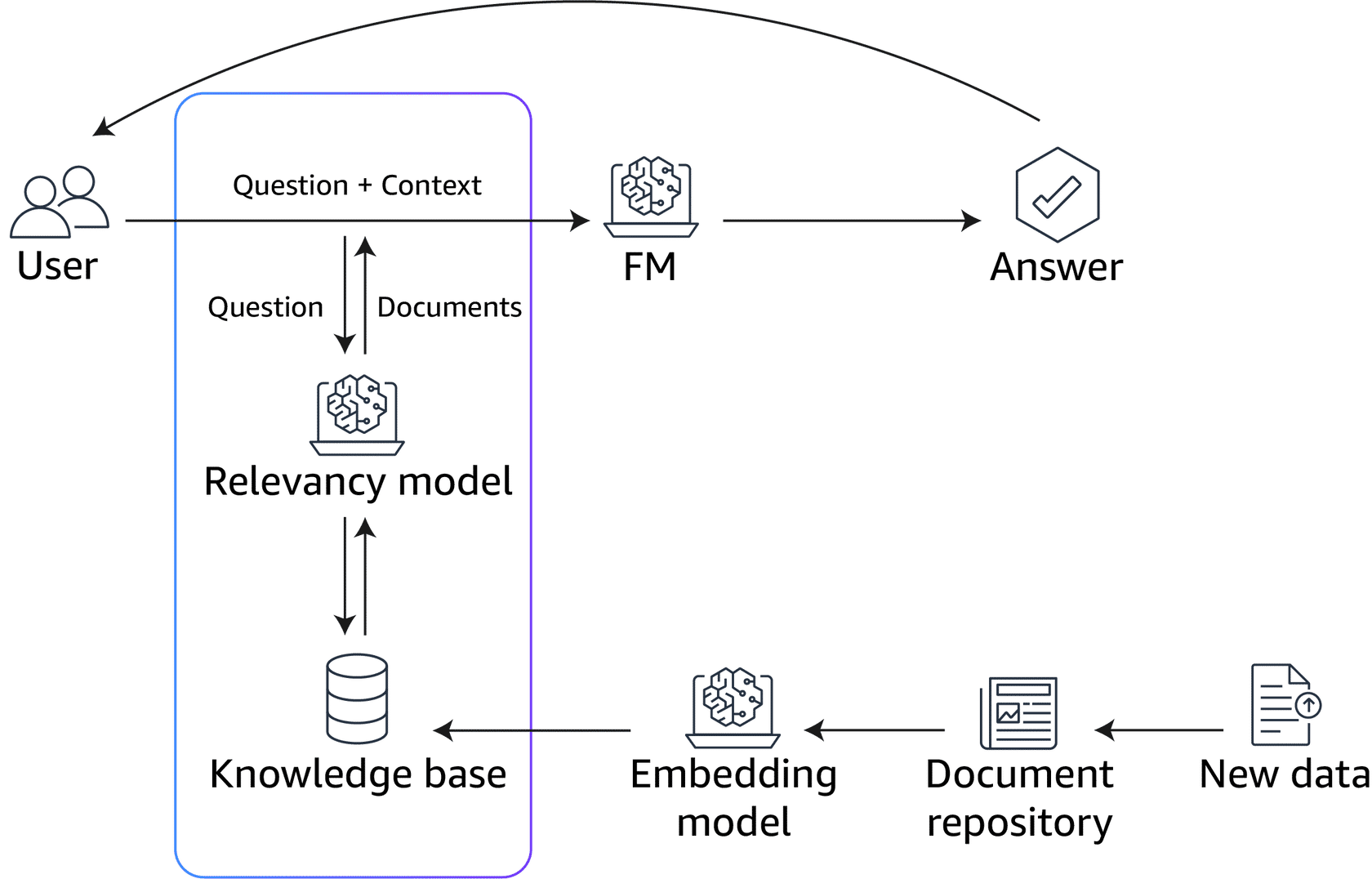
User: Encode the input text using a language model like GPT-J or Amazon Titan Embeddings.
Knowledge base: Retrieve relevant examples from a knowledge base that matches the input. These examples are encoded in the same way.
FM:Provide the enhanced prompt with question and context to the foundation model to generate a response.
Answer:The generated response is conditioned on both the input and the retrieved examples, incorporating information from multiple relevant examples into the response.

