AWS Prompt Foundation Models
Basics of Foundation Models
Generative AI creates new content and ideas, including conversations, stories, images, videos, and music.
Like all other AI, generative AI uses machine learning (ML) models.
However, generative AI uses very large models, commonly called foundation models.
FMs are pretrained on a vast corpus of data, usually through self-supervised learning.
Understanding FM functionality
The size and general-purpose nature of foundation models make them different from traditional ML models.
FMs use deep neural networks to emulate human brain functionality and handle complex tasks.
You can adapt them for a broad range of general tasks, such as text generation, text summarization, information extraction, image generation, chatbots, and question answering.
FMs can also serve as the starting point for developing more specialized models.
Examples of FMs include Amazon Titan, Amazon Nova, Meta Llama 2, Anthropic Claude, AI21 Labs Jurassic-2 Ultra, and others.
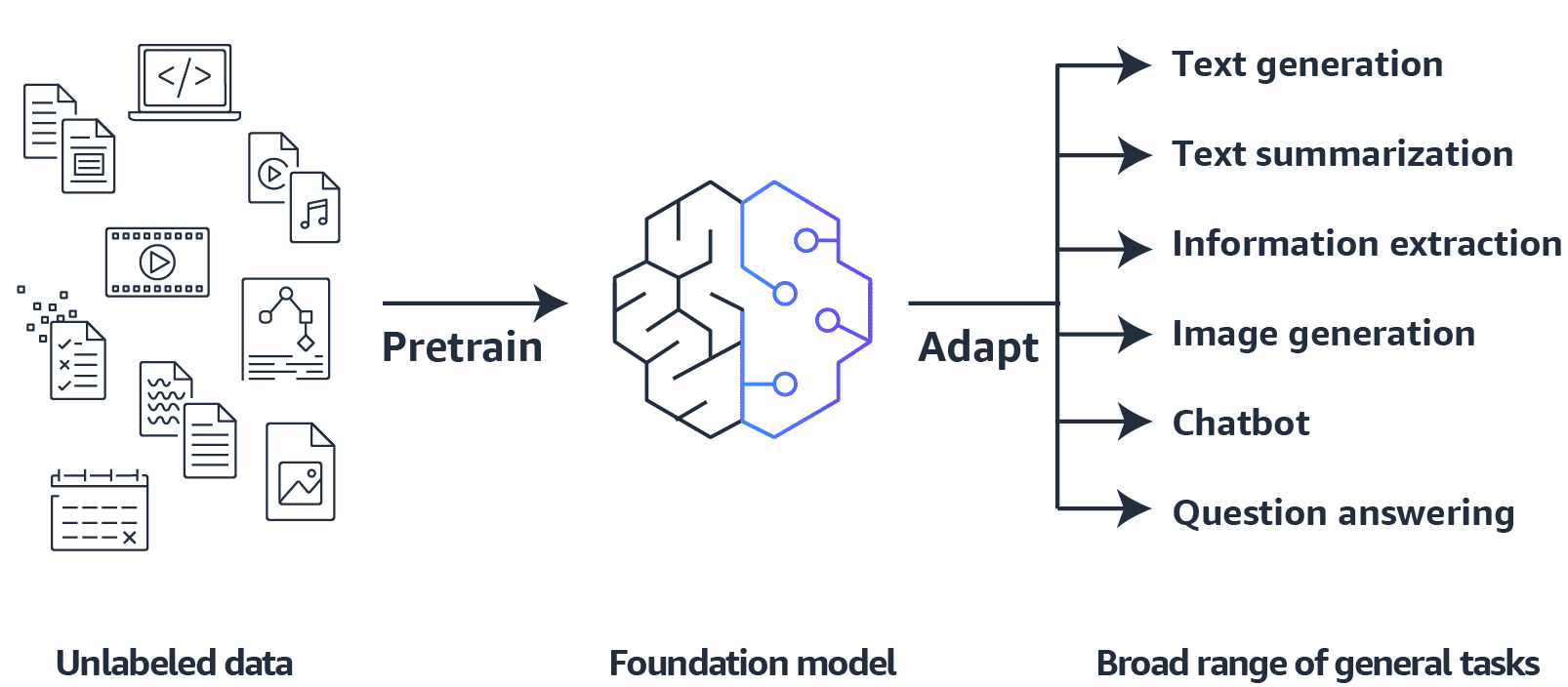
Image created by Amazon Web Services.
Self-supervised learning
Although traditional ML models rely on supervised, semi-supervised, or unsupervised learning patterns, you can see that FMs are typically pretrained through self-supervised learning.
With self-supervised learning, you don't need labeled examples.
Self-supervised learning uses the structure within the data to autogenerate labels.
Training, fine-tuning, and prompt engineering
Foundation models go through various stages of training to help you achieve the best results.
Training
During training, FMs use self-supervised learning to capture data from vast datasets. The algorithm learns the meaning, context, and relationships of words-for example, whether "drink" means a beverage (noun) or swallowing liquid (verb).
Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) can align the model with human preferences by using feedback on outcomes to adjust behavior.
Fine-tuning
Fine-tuning improves performance by adding specific, smaller datasets to a pretrained model, modifying weights to better align with the task.
Two ways to fine-tune:
- Instruction fine-tuning - Uses examples of how the model should respond to specific instructions. Prompt tuning is a type of instruction fine-tuning.
- RLHF - Provides human feedback data for better alignment with human preferences.
For example, a pretrained model can be fine-tuned with medical journal articles to achieve more contextualized results for medical research tasks.
Prompt engineering
Prompts act as instructions for foundation models. Unlike fine-tuning, prompt engineering doesn't require labeled sample data or training infrastructure-making it a more efficient way to tune LLM responses.

